Have you ever built a website only to have it crash? It may be due to the lack of a robots.txt file to guide the activities of crawlers on your site.
The Robots.txt file, when done properly, can improve your SEO rankings and boost traffic to your platform.
That’s why I have scoured the internet to bring you this ultimate guide to robots.txt files so that you can harness their SEO-boosting powers.
Let’s dive straight in.
Table of Contents
What Is a Robots.txt File?
A Robots.txt file is a text file created by webmasters to instruct search engine robots such as Google Bots on how to crawl a website when they arrive.
They are a set of rules of conduct simply for search engine bots.
The Robots.txt file instructs internet robots, otherwise recognized as web crawlers, which files or pages the site owner doesn’t want them to “crawl”.
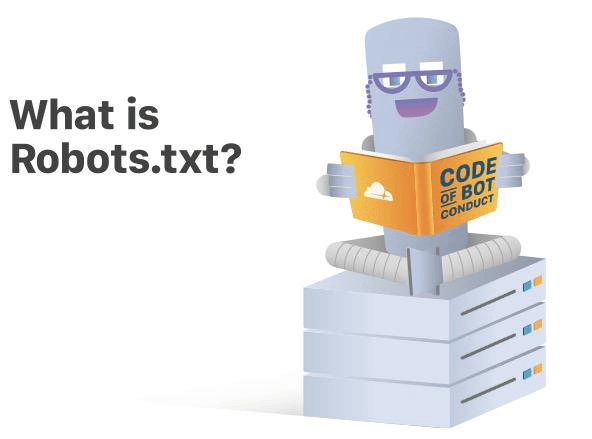
Below is what a robots.txt file looks like:
Robots.txt File – How Does It Work?
Robots.txt files are text files that lack HTML markup codes and just like every other piece of content on a website, they are housed on the server.
You can view the robots.txt file for any website by typing the full web address for the homepage and including /robots.txt.
Example:
- http://www.abcdef.com/robots.txt.
These files are not linked to any other content or location on websites, so there is a zero percent chance that your visitors will stumble upon them.
When internet crawlers access your website, before they can make your web pages feature in the search results, they have to index your files and web pages first.
That’s where robots.txt files come in. They provide the instructions for the search engine robots, giving them access to certain files and restraining or blocking them from accessing other files.
To put it another way, the robots.txt file instructs search engine crawlers or “bots” on which pages or files they can crawl and index on your website.
The files do not enforce these instructions, they only provide them. The robots will have to decide if they’ll obey the command or not.
A good bot, like a news feed bot or web crawler bot, will attempt to read the robots.txt file first before attempting to access any additional web pages and will obey the robots.txt commands.
A bad bot, on the other hand, will either dismiss the robots.txt file or filter it to find the forbidden web pages.
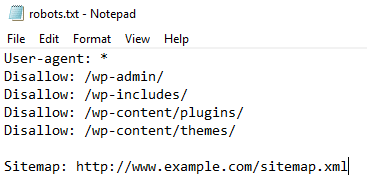
Therefore, without this file, your site would be completely naked to any web crawlers, thus awarding them entry to documents and sections you wouldn’t want the public to see.
As you can see from the above image, by using robots.txt files, you restrict web crawlers from indexing designated areas of your site.
It’s important to point out that all the subdomains on your website require robots.txt files of their own.
Therefore, to summarize, a robot.txt file helps to organize the activities of search engine bots so they don’t:
- index pages not meant for public eyes,
- overtask the server housing the website and index pages not meant for public eyes.
Importance of Robots.txt File
Here are some reasons why the robots.txt file is important and why you should use it:
The Robots.txt File Is a Guide for Web Bots.
Robots.txt files function as guides for web robots, telling them what to crawl and index and what not to.
If you create this file in the wrong compartment of your site, the crawlers will not crawl those web sections; thus, those web pages will be non-existent in the search results.
Using this file without sufficient and proper understanding can be problematic for the website.
That’s why it’s necessary to understand the purpose of robots.txt files and the proper way to use them.
Hamper Index of Resources
The Robots.txt file orders search engine crawlers not to crawl designated regions.
Meta directives can function as well as robots.txt files to deter files or sections from being indexed.
Insignificant images, scripts, or style files are suitable files that may be helpful for your site’s configuration but do not serve as “need-to-be-crawled” reserves considering they do not affect file functions.
Obstruct Non-Public Pages
Sometimes, you may need to have pages the public should not see or that robots should not index.
That could be a login page or a staging interpretation of a section.
They must remain on such pages but not be visible to the general public.
In this instance, the Robots.txt file is wielded to constrain the pages from search engines and bots.
These web pages are usually required for distinct functions on your website.
However, they don’t need to be found by every visitor coming to your website.
Optimize Crawl Budget
A crawl budget margin is when the search engine bots are incapable of indexing all of your web pages because of page congestion, copies, and any such misconceptions.
Your web pages have a hard time indexing your web pages, and it is due to crawling budget insufficiency.
Robots.txt solves this issue by simply blocking pages that are not important. If a robots.txt file is present, then Googlebot, or whichever engine is being used, can use more of your crawl budget on suitable pages.
What Subject Is Included Within a Robots.txt File?
The format in which robots.txt files provide commands or instructions is called protocols, and robots.txt protocols are of two main types, namely:
- Robots Exclusion Protocol
- Sitemaps Protocol
The Robots Exclusion Protocol is the set of instructions that tell robots which resources, files, and pages on your website they should not access. It’s the main type of protocol.
These sets of instructions are formatted and are a part of the robots.txt file.
The Sitemaps protocol is the inclusion protocol for the robots that tell search engine robots which resources, files, and web pages to crawl.
This protocol prevents robots from skipping any relevant web pages on your site.
Examples of Robots.txt Files
1. XML Sitemaps and Sitemaps Protocol
An XML sitemap is an XML file that comprises a list of all of the pages on your site alongside metadata.
It enables search engine robots to crawl across an index of all the web pages on a site in one spot.
Here is an example of what a sitemap looks like:
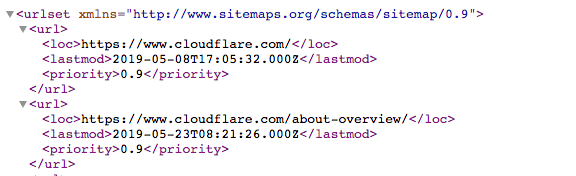
However, the sitemaps protocol tells search engine robots what they can include during a crawling session on your website.
Links to all those pages in the sitemaps are provided by the sitemap protocol and it is usually in the form of:
- Sitemap: then the URL of the XML file.
The sitemap protocol is necessary because it prevents web robots from omitting any resources when they crawl your website.
2. Robots Exclusion Protocol
The Robots.txt exclusion protocol is a set of instructions that tell search engine robots the contents, resources, files, contents, and web pages to avoid.
Below is some common robot exclusion protocol:
User-Agent Directive
The first periodic lines in each robots.txt directive are the “user-agent,” which identifies a particular bot.
The user agent is like an assigned name that an active program or person on the internet possesses.
These can be details such as the type of browser used and the version of the operating system for human users.

Personal information is not part of this detail. That helps websites provide resources, files, and other content that is relevant to the user.
For search engine robots, user agents provide webmasters with information about the types of robots that are crawling the web pages.
Through robots.txt files, webmasters instruct specific search engine robots and tell them the pages to include in the search engine results.
That is, they provide specific commands to robots of the different search engines by composing different guidelines for robot user agents.
For example, if a webmaster wants a particular piece of content displayed on Google and not Bing search engine results pages, that can be achieved by using two different sets of instructions in the robots.txt file.
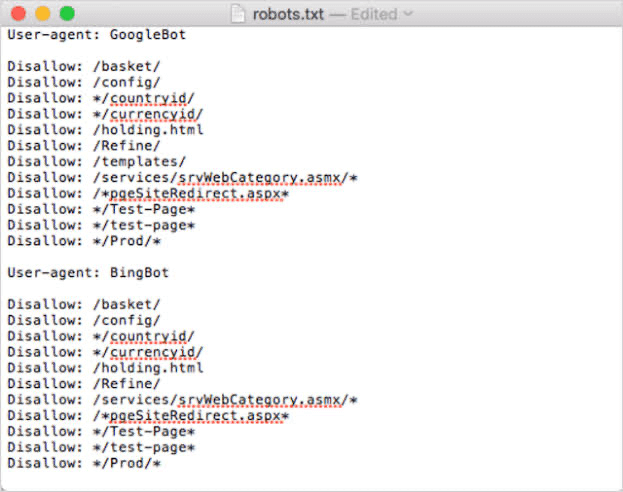
As you can see from the above example, one set of instructions is preceded by:
- User-agent: Googlebot
The other set is preceded by:
- User-agent: Bingbot
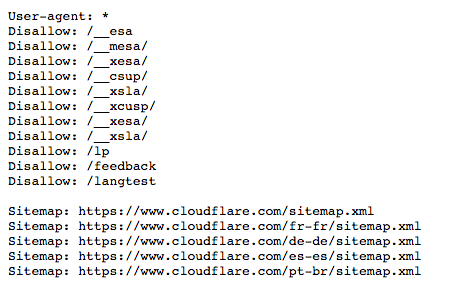
As you can see from the above example, the robots.txt file reads – “User-agent: *”.
The asterisk stands for “wild card” user agent, implying that the command is for all search engine robots and not restricted to a particular one.
The user agent names for the common search engine robots include:
Google:
- Googlebot,
- Googlebot-News (for news),
- Googlebot-Image (for images),
- Googlebot-Video (for video).
Bing
- Bingbot
- MSNBot-Media (for images and video).
Disallow Directive
This command is the most commonly used in the robot exclusion protocol.
Disallow directives tell search engine robots not to crawl certain web pages that comply with the disallow directive.

In the example above, the robots.txt file prevents all search engine robots from accessing and crawling the wp-admin page.
In most scenarios, the disallowed pages are not necessary for Bing and Google users, and it’d be time-wasting to crawl them.
Allow Directive
Allow Directives are instructions that tell search engine robots that they are permitted to access and crawl a particular directory, web page, resource, or file.
Below is an example of an allowed instruction.

Crawl-Delay Directive
The Crawl-delay directive instructs search engine robots to alter the frequency at which they visit and crawl a site so that they don’t overburden a website server.
With crawl-delay directives, a webmaster can tell the robots how long they should wait before crawling the web page, and it is mostly in milliseconds.
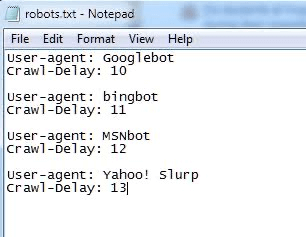
The above image shows a crawl-delay directive telling Googlebot, Bingbot, MSNbot, and Yahoo! slurp to wait for 10, 11, 12, and 13 milliseconds before requesting crawling and indexing.
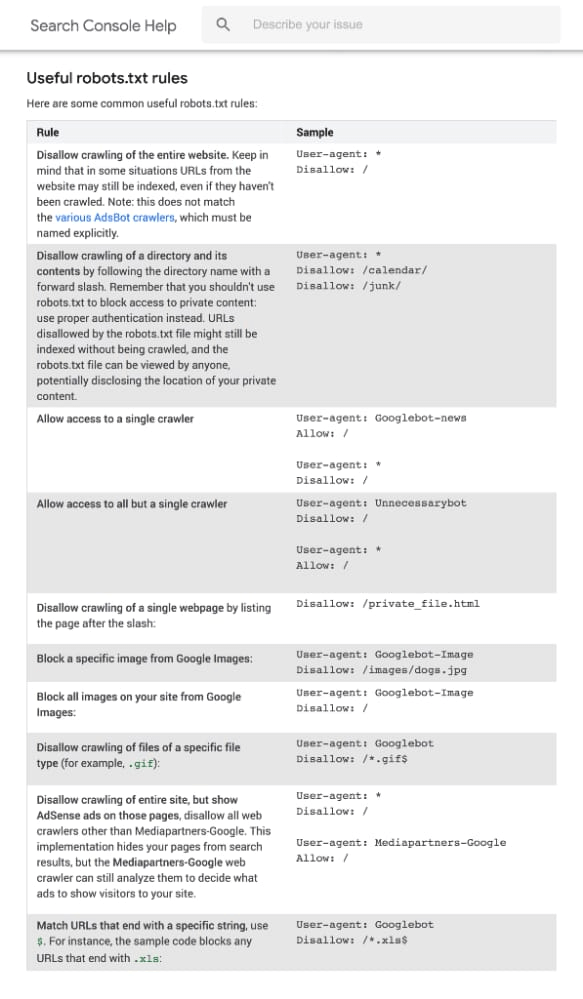
Below are some robots.txt rules and their meanings:
Understanding The Constraints of a Robots.txt File
There are constraints to this blocking method that you should understand before building a Robots.txt file.
Some limitations are as follows:
Crawlers Decipher Syntax Differently.
There is a tendency for each crawler to decipher the directives in the robots.txt file differently.
However, most credible crawlers will fulfill the commands in a robots.txt file.
It is, therefore, important to know the acceptable syntax for handling diverse web crawlers as some may not be able to decipher the instructions in robots.txt.
Some Search Engines May Not Support Robots.txt Instructions
Since the commands in robots.txt files cannot forcefully impose themselves on the response of the crawler, the web crawler has to willingly obey them.
Googlebot and other decent internet crawlers may likely obey the directives in a robots.txt file.
However, that cannot be said of other crawlers.
Therefore, if you would like to store intelligence securely, it is advisable to utilize other blocking procedures, such as protecting classified files on your server with a password.
Pages that Are Forbidden in Robots.txt Can Still Be Indexed if They Are Linked to by Other Sites
Web pages that have certain content blocked using robots.txt will not be crawled by Google.
However, if the blocked URL shares a link with other places on the internet, then it is a different thing entirely.
Search engines can locate and index it nonetheless.
Therefore, the site address and, possibly, other available data can still appear in search engine results.
To appropriately block a page from featuring in the search engine results pages, you should use the password to protect such files on your site.
You can use the response header or no-index meta tag or even eliminate the page.
Best Practices for Robots.txt
Here are some of the best practices for robots.txt:
1. Use Disallow to Curb Duplicate Content
Duplicate content happens on the web due to errors in communication and the location of the robots.txt file on your site’s page.
You can prevent duplicate content by using the “Disallow” directive to tell search engines that those copied editions of your web pages are not to be trudged upon.
Only the original content is crawled and indexed by the robots.
There, the duplicate content is obstructed.
However, if search engines can’t crawl it, it won’t be accessible to users either because of the changes in the location of files on your site.
Therefore, instead of using robots.txt to check for duplicate content, canonical tags are a good alternative to prevent crawlers from indexing duplicate pages.
So, to avoid such a traffic casualty, you can use another marker or alternative to canonicalization.
2. Create Crawlable Content
All content on your site must be important, crawlable, and relevant. Your content should not be insignificant.
Insignificant contents are statements in your site’s commands that are mistakenly duplicated or duplicate subjects, which cause search engine bots to index, grade, and crawl your site pages.
You overcome this by detailedly keeping inspections on your page’s content and the commands utilized on specific non-reliable and insignificant files that were employed in the robot.txt file.
It is done to ensure that all critical pages are crawlable and that the subject matter in them has some real significance when they are rated.
3. Specify User-Agent
User agents are texts that search engines identify themselves with. For example, Google’s robots identify themselves as Google Bots, Bing’s robots as Bingbots, and Yahoo’s robots as Slurp.
Bing bot, Google bot, Google index, and Google bot-Image are some user agents that will likely choose to ignore this robots.txt file and still process your site as a result of a corrupted file term or false page.
For your website to comprehend that you have to use similar files for most pages worldwide, the user agent ought to be defined when using the robots.txt file.
4. Inserting Robots.txt into the Root Folder
For the best SEO results, you should always keep robots.txt in the root folder.
Not keeping a robots.txt file in the root folder of a site is a very common error.
If you miss a file altogether to be transmitted on your website, Google Bots will not have the required permission to charge at first, so they will take the direction of crawling your website.
And you do not want to do that.
So, the best SEO technique for you is to set the robots.txt file in the root folder.
5. Regulate or Survey Your File’s Content
Surveying an already prevailing robots.txt file on your website, which is transmitted as the commanding edition to search engines, would help it or any other search engine to proceed sufficiently.
You should evaluate your file’s subject for the robots.txt file so that:
- Your instructions for web pages are revamped.
- You can also make certain that no subject that you want to be crawled over is obstructed.
- Skillfully furnish updated XML sitemap URLs in the subject line of the robots.txt files.
- Changing the file terms and utilizing manuals and sub-directories for commanding the search engine crawler
Conclusion
Robots.txt files are very essential weapons to have in your SEO armory.
They tell search engine robots where they can and cannot go on your website.
With this knowledge, I believe you can tap into this SEO strategy and garner better rankings for your website.